Laboratory
DRYING SHRINKAGE
PST Method

The PST Method (Plastic Sleeve Test / Polish Shrinkage Test) is an innovative research technique for measuring autogenous shrinkage and drying shrinkage of cement composites at a laboratory scale. The cement mixture is cast into plastic sleeves that prevent moisture diffusion from the sample to the environment [1]. The samples are cylindrical, with a length of 300 mm and a diameter of 25 mm (for cement pastes and mortars), 40 mm (for concrete with a maximum aggregate size dk = 8 mm), and 65 mm (for concrete with a maximum aggregate size dk = 16 mm). The cylindrical shape ensures radial and uniform drying. The sample diameters comply with the EN 12390-1 standard, which specifies that the minimum sample side should be at least 3.5 times the maximum aggregate size. Shrinkage deformations are recorded using digital dial gauges with a resolution of 2 µm or inductive sensors with a resolution of 1 µm, ensuring measurement accuracy of up to 4 µm/m. The drying shrinkage measurements are recorded automatically at controlled intervals. Currently, the laboratory is equipped with 36 digital research stations, which allow for advanced studies on the influence of various component types and compositions on the kinetics of total shrinkage in the reference composite. By simultaneously measuring total shrinkage and autogenous shrinkage, the portion of deformations attributable to drying shrinkage can be isolated. The tests are conducted in constant temperature and humidity conditions: 20±2°C and 50±5% RH. Testing can also be performed under controlled ambient temperature and humidity conditions, with temperature measurements taken from the samples. The PST method is patent-pending [2]. It is currently standardized under the AASHTO standard in the United States. Below is an example of a measurement:
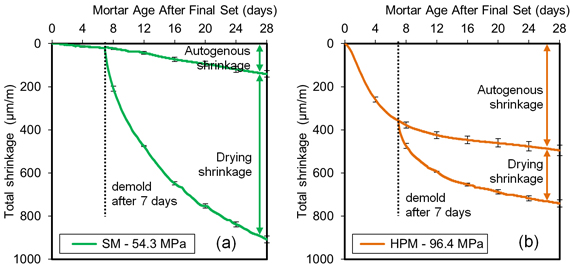
Development of autogenous shrinkage and drying shrinkage in cement mortars: (a) standard mortar, (b) high-performance mortar [1].
-------------------------
[1] A. Zieliński, A.K. Schindler, 2024. Plastic-Sleeve Test Method to Measure Autogenous and Drying Shrinkage in Paste, Mortar, and Concrete: Test Results, Measurement 237, 115138. DOI: 10.1016/j.measurement.2024.115138
[2] A. Zieliński. Method of forming a sample for testing the deformation of autogenous materials with a matrix based on a mineral or organic binder in the early and late maturation stage and a stand for this forming. Polish patent PL244502, registered on 11.06.2019 and published 05.02.2024. https://patents.google.com/patent/PL244502B1
Dilatometric method acc. to EN 12390-16:2020-03

The procedure for testing volumetric changes in cement composites due to drying is standardized in Polish industry standards: the Graf-Kaufman method (PN-B-06714/24:1984 – vertical measurement) and the Amsler method (PN-B-06714/23:1984 – horizontal measurement). The current standard, PN-EN 12390-16:2020-03, is based on the Graf-Kaufman method. Shrinkage deformations are measured on prismatic or cylindrical samples placed in molds. After one day, the samples are demolded and placed in a dilatometer. Shrinkage deformations are recorded manually or automatically at controlled intervals. At present, the laboratory is equipped with 12 digital test stations, capable of molding prismatic samples with dimensions of 40x40x160 mm and 50x50x250 mm (for vertical measurement) and 100x100x400 mm (for horizontal measurement). The tests are carried out in constant temperature and humidity conditions: 20±2°C and 50±5% RH. Tests can also be performed at controlled ambient temperatures and humidity. Below is an example of a measurement:
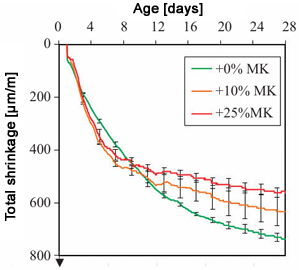
The effect of metakaolin on the development of total shrinkage in cement mortars with a w/s ratio of 0.5 [3].
-------------------------
[3] A. Zieliński, P. Wolka, W. Żebrowski, The effect of metakaolin addition on autogenous and total shrinkage of materials with a cement matrix, Materiały budowlane 12/2022. DOI: 10.15199/33.2022.12.33



